In our unpredictable world, insurance provides a vital safety net, offering financial protection against unforeseen events. Whether it’s for health, life, vehicles, or property, insurance helps mitigate the financial risks of life’s uncertainties. In this blog, we will delve into the basics of insurance, types of insurance, and why it is important.
What is Insurance?
Insurance is a contract between an individual or entity (the policyholder) and an insurance company. The policyholder pays a premium, and in return, the insurance company agrees to cover financial losses related to specific risks as outlined in the insurance policy. The fundamental purpose of insurance is to spread the risk among many policyholders to ensure that no one person bears the full financial burden of a significant loss.

How Does Insurance Work?
When you buy insurance, you pay a regular premium to the insurer. In the event of a loss covered under the policy (such as a car accident, medical emergency, or home damage), you file a claim with your insurer. The insurer reviews the claim and, if it is valid, compensates you for the loss as per the policy terms.
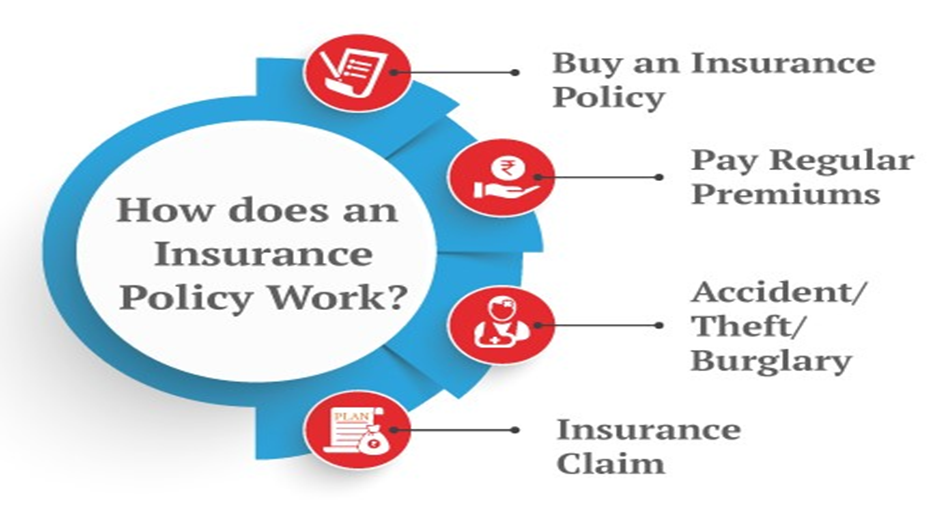
Key Elements of Insurance

1. Premium: This is the amount you pay, either monthly or annually, to keep the insurance policy active.
2. Policy: The document that outlines the terms, conditions, coverage, and exclusions of the insurance agreement.
3. Deductible: The amount you must pay out of pocket before your insurance coverage kicks in. Higher deductibles often lead to lower premium costs.
4. Coverage Limit: This is the maximum amount the insurer will pay for a covered claim. Anything above this limit must be borne by the policyholder.
Types of Insurance
There are many types of insurance, each designed to cover different aspects of life:
1. Health Insurance: This covers medical expenses, hospital stays, surgeries, and sometimes even medication. Health insurance ensures that you don’t face financial ruin in the event of a serious illness or accident.
2. Life Insurance: Life insurance provides a payout to your beneficiaries upon your death. It helps protect your family from financial difficulties if they depend on your income.
3. Auto Insurance: Mandatory in many places, auto insurance protects against financial loss in the case of an accident, theft, or damage to your vehicle.
4. Homeowners or Property Insurance: This insurance protects your home or property from risks such as fire, theft, or natural disasters. It helps you recover financially if your property is damaged or destroyed.
5. Travel Insurance: This offers coverage for travel-related issues such as medical emergencies, trip cancellations, lost luggage, or flight delays.
6. Disability Insurance: If an injury or illness prevents you from working, disability insurance provides a portion of your income during the time you are unable to work.
7. Liability Insurance: This protects you against legal liabilities if someone sues you for damages caused by your actions, whether intentional or accidental.
Importance of Insurance
1. Financial Security: Insurance protects individuals and businesses from financial hardships caused by unexpected events. Without insurance, a single unfortunate event could wipe out your savings or lead to massive debt.
2. Risk Management: Insurance spreads out risks among a large pool of policyholders, reducing the financial burden on any one person. It provides peace of mind, knowing that you are protected in case of emergencies.
3. Promotes Savings: Some types of insurance, such as whole life insurance, also act as savings or investment tools. They allow you to build cash value over time, which you can use in the future.
4. Encourages Responsibility: Many people buy insurance to comply with legal requirements (e.g., auto insurance) or to provide security for loved ones. It encourages individuals to think about long-term financial planning.

Factors Affecting Insurance Premiums
1. Age: Older individuals tend to pay higher premiums for life and health insurance due to a higher risk of illness or death.
2. Location: Your home’s location can affect your premiums for home insurance. Areas prone to natural disasters or with higher crime rates may have higher premiums.
3. Health and Lifestyle: Healthier individuals, non-smokers, and those with lower-risk lifestyles often get better rates on life and health insurance.
4. Claims History: If you have a history of making multiple claims, insurers may view you as a higher risk and increase your premiums.
5. Coverage Amount: The more coverage you want, the higher your premium will be. Additionally, policies with lower deductibles often come with higher premiums.
Conclusion
Insurance is an essential tool for financial planning and risk management. It protects individuals and businesses from the potentially devastating costs associated with accidents, illness, property damage, or loss of life. By understanding how insurance works and selecting the right types of coverage for your needs, you can secure a safer and more financially stable future.
